-
BONEDIET PLUS TAB 10`S ₦3,073.25 QTY: 1
-
Anusol Suppositories - 12/24 Pack ₦26,600.00 QTY: 1
-
GLIMP M2 SR TAB 10`S ₦2,894.25 QTY: 3
-
Green World Livergen Capsule ₦18,000.00 QTY: 1
-
Natures Aid Collagen Joint Formula - 60 Pack ₦44,900.00 QTY: 1
-
EPINEXT 500MG STRIP OF 10 TABLETS ₦1,650.00 QTY: 1
-
Imodium 2mg 6 capsules ₦1,050.00 QTY: 1
-
EUREPA 2MG TABLET 15?S ₦8,518.25 QTY: 1
-
IVANODE C 6.25 Tablet 10?s ₦37,400.00 QTY: 1
-
SODIUM BICARBONATE(T.WALKERS) 7.5% Injection 25ml ₦23,800.00 QTY: 2
-
DELTONE 60MG CAP 10`S ₦4,476.50 QTY: 1
-
DYLOOP 10MG STRIP OF 15 TABLETS ₦1,423.25 QTY: 1
-
Klorane Ultra-gentle Shampoo with Oat 200ml ₦25,511.11 QTY: 1
-
Sideral GOCCE Drops 30ml ₦49,776.00 QTY: 1
-
Juvela Low Protein Bread Mix ₦93,300.00 QTY: 1
-
KINDERZYME Syrup 200ml ₦37,400.00 QTY: 1
-
MOVALITH 400mg Tablet 10?s ₦23,800.00 QTY: 1
-
Spiruviva Food Supplement 540 Tablets ₦72,675.00 QTY: 1
-
Manuka Honey MGO400+ 250 g ₦112,240.00 QTY: 1
-
Dewderm Soap - 100 g (Pack of 3) ₦4,800.00 QTY: 1
-
Bomastren 750 mg Injection 3ml ₦586,500.00 QTY: 1
Customer matched zone "Lagos Delivery Options"
Sort by:
117793–117808 of 373020 Results
-
EXCEDRIN EXTRA STRENGTH PAIN RELIEF CAPLETS, WHITE, 24 COUNTSku: 1718621978-2239
EXCEDRIN EXTRA STRENGTH PAIN RELIEF CAPLETS, WHITE, 24 COUNT
₦22,700.00 -
Additional information Reviews (0) Weight 0.000000 kg Dimensions 0.000000 × 0.000000 × 0.000000 cm Reviews There are no reviews yet. Write a review Cancel replyYou must be logged in to post a review.Sku: 8375
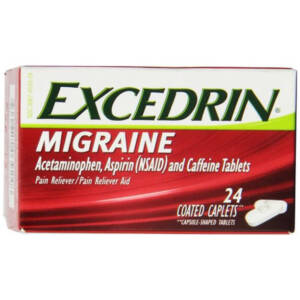
EXCEDRIN MIGGRAINE 24CAP
₦8,100.00 -
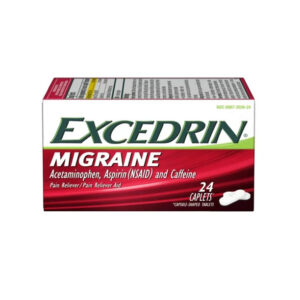
Excedrin Migraine Drugs 0 The AllschoolabsStars rating goes beyond a simple average of reviews. It?s calculated based on various factors, including the quantity, recency, and reliability of the reviews. Read More Search for medical details concerning Excedrin Migraine oral on Allschoolabs including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings and user ratings. Ask a Question Write a reviewSku: 1742126355-829
Excedrin Migraine
₦0.00 -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
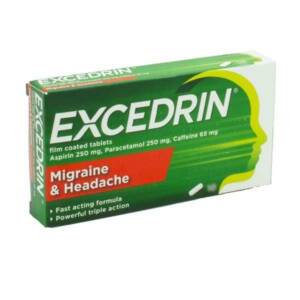
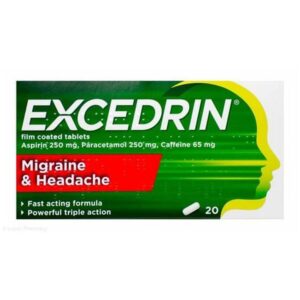
Excedrin Migrane & Headache Tablets 20 PackSku: 1731836720-2183
Excedrin Migrane & Headache Tablets 20 Pack
₦0.00