-
GALVUSMET 50/500MG TAB 15?S ₦6,767.00 QTY: 1
-
BOSUVI 400mg Tablet 30?s ₦508,300.00 QTY: 1
-
GLADOR M 2MG FORTE TAB 15`S ₦4,913.00 QTY: 1
-
EPNONE T 10 COMBIKIT STRIP OF 20 TABLETS ₦4,755.75 QTY: 3
-
DIGENE GEL MINT SYP 200ML ₦2,984.25 QTY: 2
-
Skin Care Cellufit Action Food Supplement 60 Capsules ₦58,463.00 QTY: 2
-
NUHB Syrup 200ml ₦30,600.00 QTY: 2
-
ENVAS 2.5MG TABLET ₦1,351.25 QTY: 2
-
Anbesol Adult Strength Gel - 10g (A) ₦2,750.00 QTY: 1
-
Dermalogica Sound Sleep Cocoon Night Gel-Cream 50ml ₦204,453.35 QTY: 1
-
Siar Pharma Althemol Oral Solution 200ml ₦22,021.00 QTY: 5
-
Docel 120mg Injection 1?S ₦678,300.00 QTY: 1
-
AFDURA TAB 10`S ₦6,901.00 QTY: 1
-
CILAMET XL 20/50MG TAB ₦5,994.50 QTY: 3
-
G FORMIN PLUS TABLET ₦1,031.25 QTY: 2
-
CILDIP 5MG TAB 10`S ₦1,299.50 QTY: 1
-
KITAVA ACNE BUSTER Gel 50ml ₦49,300.00 QTY: 1
-
CIPGEST 2MG TAB 10`S ₦12,389.00 QTY: 2
-
PINOM H 20MG TABLET 15?S ₦4,397.25 QTY: 1
-
YOGI CHURNA (35g) ₦760.00 QTY: 1
-
Asaq 6-13yrs ₦1,560.00 QTY: 1
-
Denrit 250mg Tablet 10?S ₦187,000.00 QTY: 1
-
GLIMP M1 TAB 10`S ₦1,802.50 QTY: 1
-
Formosone 250 Respicap 30?S ₦49,300.00 QTY: 4
-
DUTAJOY 0.5MG STRIP OF 10 TABLETS ₦3,052.50 QTY: 1
-
Evermil 5mg Tablet 10?S ₦270,300.00 QTY: 2
-
Brintop F 5% Topical Solution, 100ML ₦9,300.00 QTY: 1
-
MAXIFLO 250MCG BOX OF 120MD METERED DOSE INHALER ₦11,319.18 QTY: 1
-
DROTIN DS MANGO FLAVOUR SUGAR FREE BOTTLE OF 100ML SUSPENSION ₦6,079.50 QTY: 1
-
FERBIN Suspension 150ml ₦30,600.00 QTY: 2
-
ALKASTON B6 200ML SOLUTION ₦4,305.50 QTY: 1
-
Leukoplast Adhesive Tape - 1.25cm x 5m ₦5,000.00 QTY: 2
-
OZEPRO 1% TUBE OF 5GM CREAM ₦2,554.50 QTY: 1
-
FEBSMART 40MG STRIP OF 10 TABLETS ₦1,835.75 QTY: 2
-
Pebind 400mg Tablet ₦1,345.00 QTY: 1
-
GLUCONORM VG 1MG TAB 15`S ₦5,238.50 QTY: 1
-
Vitabiotics Pregnacare Original - 30 or 90 Pack ₦11,900.00 QTY: 2
-
BRITE Wite Skin Brightening and Lightening Cream (30 gm) ₦5,450.00 QTY: 2
-
Cerokids Appetite Stimulant Syrup ₦900.00 QTY: 2
-
CILNEP 10MG TAB 10`S ₦1,648.00 QTY: 2
-
FIGOMET SR 1 TABLETS 10?S ₦788.00 QTY: 1
-
DAILY IRON SR TABLETS 15?S ₦1,670.75 QTY: 1
-
Curaprox Be you Toothpaste Peach+Apricot 60ml ₦31,232.00 QTY: 1
-
PENTOWOK D TABLET ₦2,451.50 QTY: 2
-
FUNGIKEM 100MG CAP 7`S ₦0.00 QTY: 1
-
Fungicros Cream ₦100.00 QTY: 1
-
FUR TOTAL TABLET ₦3,652.75 QTY: 1
-
DILNIP 20MG STRIP OF 10 TABLETS ₦5,361.50 QTY: 1
-
TOBROMEL 400 60CPR ₦36,442.00 QTY: 1
-
MELACARE ACNE Gel 15gm ₦40,800.00 QTY: 1
-
Scholl Air Pillow Comfort Insoles- Provide Comfort & Prevent Foot Pain ₦11,000.00 QTY: 2
-
FERTOMID 100MG TABLET ₦1,499.75 QTY: 1
-
CITICOP P Tablet 10?s ₦57,800.00 QTY: 2
-
Novolizer Device 1?S ₦42,500.00 QTY: 1
-
Pirox Conditioner 150ml ₦1,795.00 QTY: 1
-
DEZACOR 30MG TAB 6`S ₦7,622.00 QTY: 1
-
ROBINAXOL TABLET ₦1,979.00 QTY: 1
-
EPLEHEF 25MG TAB 10`S ₦4,202.50 QTY: 2
-
PRICHEK M 2MG STRIP OF 10 TABLETS ₦3,588.75 QTY: 1
-
CARIPAYA TAB 10`S ₦9,673.25 QTY: 1
-
CEPOVO 100MG 30ML SYP ₦3,155.75 QTY: 1
-
CEFOLAC CV 50MG 30ML SUSP ₦2,330.75 QTY: 1
-
Geske MicroCurrent Skin Scrubber & Blackhead Remover 9 in 1 ₦72,816.00 QTY: 1
-
CARBOPLATIN 150mg Injection 15ml ₦71,400.00 QTY: 2
-
CTD M 6.25/50MG TAB 10`S ₦2,341.25 QTY: 1
-
Curlz-F 5% Solution, 60ml ₦5,700.00 QTY: 1
-
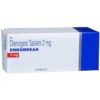
ENDOBREAK 2MG TABLETS 10?S ₦13,379.50 QTY: 1
-
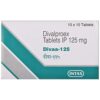
DIVALEX OD 125MG TAB 10`S ₦975.00 QTY: 2
-
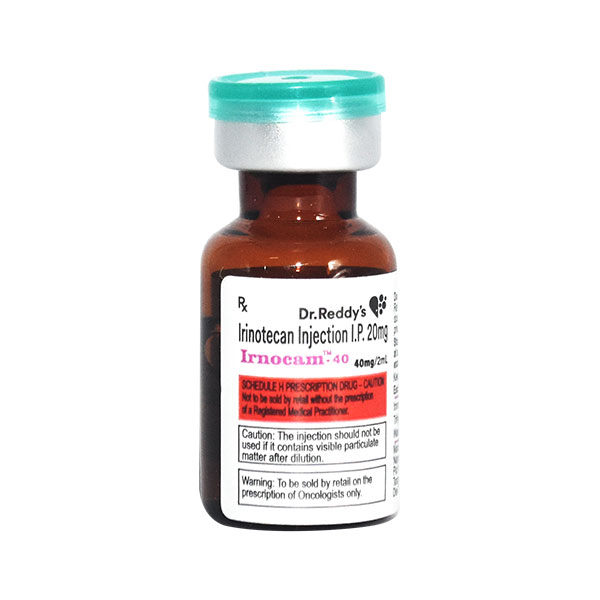
Irnocam 40mg Injection 2ml ₦68,000.00 QTY: 1
Customer matched zone "Lagos Delivery Options"
“DIVALEX OD 125MG TAB 10`S” has been added to your basket. Continue shopping
“ENVAS 2.5MG TABLET” has been added to your basket. Continue shopping
“EPLEHEF 25MG TAB 10`S” has been added to your basket. Continue shopping
Sort by:
273–288 of 4627 Results
-
SaleAxxo 0.05%+0.75%+2%+1%This cream is indicated in the treatment of- Mixed and complicated Fungal, Protozoal & Bacterial infections, Mild to moderate vaginitis, Candidiasis and trichomoniasis, Pruritus vulvae, Dermatitis, Eczema, Genito-urinary infections. CompositionEach gram cream contains- Clobetasol Propionate USP 0.50 mg Ofloxacin USP 7.50 mg Ornidazole INN 20 mg Terbinafine Hydrochloride BP 10 mg Theropeutic ClassClobetasol / Clobetasone & Combined PreparationsPharmacologyThis cream is a combination cream which exhibits anti-bacterial, anti-fungal, anti-protozoal & anti-inflammatory actions. Clobetasol is a potent corticosteroid which exhibits anti-inflammatory, anti-pruritic and vasoconstrictive properties. Ofloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that acts against many gram-positive & gram-negative bacteria. Ornidazole belongs to the nitroimidazole group of antibiotics and is used to treat amoeba and trichomonas infections. Terbinafine is an Allylamine antifungal that inhibits biosynthesis of Ergosterol (an essential components if fungal cell membrane) via inhibition of Squalene Epoxidase enzyme causing fungal cell death. Dosage & Administration of Axxo 0.05%+0.75%+2%+1%Apply by gently rubbing onto the affected area twice daily.Dosage of Axxo 0.05%+0.75%+2%+1%Apply by gently rubbing onto the affected area twice daily.Interaction of Axxo 0.05%+0.75%+2%+1%No hazardous interactions have been reported.ContraindicationsContraindicated in patients hypersensitive to any of the components of the formulation.Side Effects of Axxo 0.05%+0.75%+2%+1%Burning, itching, irritation, dry skinPregnancy & LactationThe safe use of this preparation during pregnancy & lactation has not been established.Precautions & WarningsDo not shallow. For external use onlyStorage ConditionsStore below 30?C. keep away from light and out of the reach of children. Do not freeze.Drug ClassesClobetasol / Clobetasone & Combined PreparationsMode Of ActionThis cream is a combination cream which exhibits anti-bacterial, anti-fungal, anti-protozoal & anti-inflammatory actions. Ofloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that acts against many gram-positive & gram-negative bacteria. Ornidazole belongs to the nitroimidazole group of antibiotics and is used to treat amoeba and trichomonas infections. Terbinafine is an Allylamine antifungal that inhibits biosynthesis of Ergosterol (an essential components if fungal cell membrane) via inhibition of Squalene Epoxidase enzyme causing fungal cell death. Clobetasol is a potent corticosteroid which exhibits anti-inflammatory, anti-pruritic and vasoconstrictive properties.PregnancyThe safe use of this preparation during pregnancy & lactation has not been established.Sku: 1736098333-1764
Axxo0.05%+0.75%+2%+1%
₦8,250.00Original price was: ₦8,250.00.₦7,425.00Current price is: ₦7,425.00.₦8,250.00Original price was: ₦8,250.00.₦7,425.00Current price is: ₦7,425.00. Add to basket Quick View -
SaleAZ 500 mgAZ 500 mg is prescribed for infections (produced by susceptible organisms) in the upper respiratory tract, including sinusitis and pharyngitis/tonsillitis, the lower respiratory tract, including bronchitis and pneumonia, the otitis media, and the skin and soft tissue. AZ 500 mg is recommended for the treatment of non-gonococcal urethritis and cervicitis caused by Chlamydia trachomatis in sexually transmitted illnesses in both men and women.Theropeutic ClassMacrolidesPharmacologyAZ 500 mg belongs to the macrolide subclass of antibiotics known as azalide. In order to prevent microbial protein synthesis, AZ 500 mg binds to the 50s ribosomal subunit of susceptible species. Moraxella catarrhalis, anaerobes such as Bacteroides fragilis, Escherichia coli, Bordetella pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis, Borrelia burgdorferi, Haemophilus ducreyi, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae, as well as gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, Streptoc Moreover, in vitro testing of AZ 500 mg shown action against Campylobacter sp., Toxoplasma gondii, Treponema pallidum, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Legionella pneumophila, and hominins.Dosage of AZ 500 mgAdult: 500 mg once daily orally for 3 days or 500 mg once on day 1, then 250 mg once on days 2-5 for 4 days. For sexually transmitted diseases caused by Chlamydia trachomatis in adults, the dose is 1 gm given as a single dose or 500 mg once on day 1, followed by 250 mg once daily for next 2 days may also be given. Children: 10 mg/kg body weight once daily for 3 days for child over 6 months 200 mg (1 teaspoonful) for 3 days if body weight is 15-25 kg 300 mg (1? teaspoonfuls) for 3 days if body weight is 26-35 kg; 400 mg (2 teaspoonfuls) for 3 days if body weight is 36-45 kg. In typhoid fever, 500 mg (21/2 teaspoonfuls) once daily for 7-10 days is given.Administration of AZ 500 mgProcedure for reinstatement after suspension- Step 1: Thoroughly shake the bottle to break up the powder. Step 2: Fill the bottle with boiled and cooled water to the watermark on the label. Step 3: Mix the powder and water thoroughly to combine. Take AZ 500 mg at least one hour before or two hours after eating.Interaction of AZ 500 mgWhen food and antacids are present, AZ 500 mg absorption is lessened. Due to the potential for ergotism brought on by an interaction between AZ 500 mg and the cytochrome P-450 system, AZ 500 mg should be avoided in patients who are receiving ergot alkaloids. With co-administration, care should be taken since macrolides raise the plasma levels of cyclosporin and digoxin. Warfarin, Theophylline, Carbamazepine, Methylprednisolone, or Cimetidine have not been found to interact with AZ 500 mg.ContraindicationsThose who are hypersensitive to AZ 500 mg or any other macrolide antibiotic should not take AZ 500 mg. Ergot derivatives and AZ 500 mg should not be administered together. Those with liver disorders should not use AZ 500 mg.Side Effects of AZ 500 mgLow-frequency side effects are experienced after taking AZ 500 mg. A therapeutic withdrawal will reverse the adverse effects, which include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain or cramps, flatulence, diarrhea, headaches, and skin rashes.Pregnancy & LactationThe AZ 500 mg pregnancy category is B. Studies on animal reproduction have shown that AZ 500 mg has no evidence of harming the fetus. Pregnant women have not been the subject of any good, controlled studies. AZ 500 mg should only be used during pregnancy if no other suitable options are available, as research on animal reproduction are not always indicative of human response. The presence of AZ 500 mg in breast milk is unknown. Hence, when giving AZ 500 mg to nursing mothers, care should be taken.Precautions & WarningsIt is advised to keep an eye out for any superinfection with non-susceptible organisms, such as fungus when using any antibiotic. Those with renal impairment don't require a dose adjustment.Overdose Effects of AZ 500 mgThere is no information on AZ 500 mg overdosage. Macrolide antibiotic overdose symptoms can include hearing loss, extreme nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. The use of gastric lavage and other supportive treatments is advised.Storage ConditionsKeep dry and away from heat and light. Keep out of children's reach.Sku: 1736106142-4059
AZ500 mg
₦3,025.00Original price was: ₦3,025.00.₦2,752.75Current price is: ₦2,752.75.₦3,025.00Original price was: ₦3,025.00.₦2,752.75Current price is: ₦2,752.75. Add to basket Quick View -
SaleAzaltic 500 mgAzaltic 500 mg is prescribed for infections (produced by susceptible organisms) in the upper respiratory tract, including sinusitis and pharyngitis/tonsillitis, the lower respiratory tract, including bronchitis and pneumonia, the otitis media, and the skin and soft tissue. Azaltic 500 mg is recommended for the treatment of non-gonococcal urethritis and cervicitis caused by Chlamydia trachomatis in sexually transmitted illnesses in both men and women.Theropeutic ClassMacrolidesPharmacologyAzaltic 500 mg belongs to the macrolide subclass of antibiotics known as azalide. In order to prevent microbial protein synthesis, Azaltic 500 mg binds to the 50s ribosomal subunit of susceptible species. Moraxella catarrhalis, anaerobes such as Bacteroides fragilis, Escherichia coli, Bordetella pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis, Borrelia burgdorferi, Haemophilus ducreyi, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae, as well as gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, Streptoc Moreover, in vitro testing of Azaltic 500 mg shown action against Campylobacter sp., Toxoplasma gondii, Treponema pallidum, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Legionella pneumophila, and hominins.Dosage of Azaltic 500 mgAdult: 500 mg once daily orally for 3 days or 500 mg once on day 1, then 250 mg once on days 2-5 for 4 days. For sexually transmitted diseases caused by Chlamydia trachomatis in adults, the dose is 1 gm given as a single dose or 500 mg once on day 1, followed by 250 mg once daily for next 2 days may also be given. Children: 10 mg/kg body weight once daily for 3 days for child over 6 months 200 mg (1 teaspoonful) for 3 days if body weight is 15-25 kg 300 mg (1? teaspoonfuls) for 3 days if body weight is 26-35 kg; 400 mg (2 teaspoonfuls) for 3 days if body weight is 36-45 kg. In typhoid fever, 500 mg (21/2 teaspoonfuls) once daily for 7-10 days is given.Administration of Azaltic 500 mgProcedure for reinstatement after suspension- Step 1: Thoroughly shake the bottle to break up the powder. Step 2: Fill the bottle with boiled and cooled water to the watermark on the label. Step 3: Mix the powder and water thoroughly to combine. Take Azaltic 500 mg at least one hour before or two hours after eating.Interaction of Azaltic 500 mgWhen food and antacids are present, Azaltic 500 mg absorption is lessened. Due to the potential for ergotism brought on by an interaction between Azaltic 500 mg and the cytochrome P-450 system, Azaltic 500 mg should be avoided in patients who are receiving ergot alkaloids. With co-administration, care should be taken since macrolides raise the plasma levels of cyclosporin and digoxin. Warfarin, Theophylline, Carbamazepine, Methylprednisolone, or Cimetidine have not been found to interact with Azaltic 500 mg.ContraindicationsThose who are hypersensitive to Azaltic 500 mg or any other macrolide antibiotic should not take Azaltic 500 mg. Ergot derivatives and Azaltic 500 mg should not be administered together. Those with liver disorders should not use Azaltic 500 mg.Side Effects of Azaltic 500 mgLow-frequency side effects are experienced after taking Azaltic 500 mg. A therapeutic withdrawal will reverse the adverse effects, which include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain or cramps, flatulence, diarrhea, headaches, and skin rashes.Pregnancy & LactationThe Azaltic 500 mg pregnancy category is B. Studies on animal reproduction have shown that Azaltic 500 mg has no evidence of harming the fetus. Pregnant women have not been the subject of any good, controlled studies. Azaltic 500 mg should only be used during pregnancy if no other suitable options are available, as research on animal reproduction are not always indicative of human response. The presence of Azaltic 500 mg in breast milk is unknown. Hence, when giving Azaltic 500 mg to nursing mothers, care should be taken.Precautions & WarningsIt is advised to keep an eye out for any superinfection with non-susceptible organisms, such as fungus when using any antibiotic. Those with renal impairment don't require a dose adjustment.Overdose Effects of Azaltic 500 mgThere is no information on Azaltic 500 mg overdosage. Macrolide antibiotic overdose symptoms can include hearing loss, extreme nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. The use of gastric lavage and other supportive treatments is advised.Storage ConditionsKeep dry and away from heat and light. Keep out of children's reach.Sku: 1736100641-2447
Azaltic500 mg
₦1,925.00Original price was: ₦1,925.00.₦1,732.50Current price is: ₦1,732.50.₦1,925.00Original price was: ₦1,925.00.₦1,732.50Current price is: ₦1,732.50. Add to basket Quick View -
SaleAzelec 20%Azelec 20% cream is indicated for the topical treatment of mild to moderate inflammatory acne vulgaris.Theropeutic ClassAcne treatment preparationsPharmacologyAzelaic acid is a naturally-occurring aliphatic dicarboxylic acid that inhibits the growth of Propionibacterium acnes and reduces keratinisation, thus restricts the development of comedones.Dosage & Administration of Azelec 20%Acne vulgaris: Adult: As 20% cream or 15% gel: Apply thinly into the affected areas bid (morning and evening) after cleansing. Improvement may be detectable w/n 4 wk. Duration of treatment: Up to 6 mth. Child: ?12 yr Same as adult dose. Rosacea: Adult: As 15% gel: Apply thinly into the affected areas bid (morning and evening). Improvement occurs in 4-8 wk. Child: ?12 yr Same as adult dose. Dosage of Azelec 20%After the skin is thoroughly washed and patted dry, a thin film of Azelec 20% should be gently but thoroughly massaged into the affected areas twice daily, in the morning and evening. The hands should be washed following application. Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients under 12 years of age have not been established. Or as directed by the physician.Interaction of Azelec 20%Avoid spicy foods, alcoholic beverages and hot drinks that might provoke erythema, flushing and blushing during treatment of rosacea.ContraindicationsAzelaic acid is contraindicated in individuals who have shown hypersensitivity to any of its components.Side Effects of Azelec 20%Local skin irritation (e.g. erythema, scaling, itching or burning) occurs in occasional cases, usually at the start of treatment. However, in the majority of cases the irritation is mild and regresses as treatment continues.Pregnancy & LactationPregnancy?Category B. Either animal-reproduction studies have not demonstrated a fetal risk but there are no controlled studies in pregnant women or animal-reproduction studies have shown an adverse effect (other than a decrease in fertility) that was not confirmed in controlled studies in women in the 1st trimester (and there is no evidence of a risk in later trimesters).Precautions & WarningsFor external use only. If Azelaic acid comes into contact with the eyes they should immediately be thoroughly rinsed with copious amounts of water. The patients should consult a physician if eye irritation persists.Storage ConditionsStore in a cool & dry place protected from light. Keep ail medicines out of reach of children.Drug ClassesAcne treatment preparationsMode Of ActionAzelaic acid has been shown to possess antimicrobial activity against Propionibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus epidennidis. The antimicrobial action may be attributable to the inhibition of microbial cellular protein synthesis. A normalization of keratinization leading to an anticomedonal effect of Azelaic acid may also contribute to its clinical activity.PregnancyFDA Pregnancy Category B. This drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed. Caution should be exercised when Azelaic acid is administered to a nursing mother.Sku: 1736104608-3606
Azelec20%
₦4,153.05Original price was: ₦4,153.05.₦3,737.80Current price is: ₦3,737.80.₦4,153.05Original price was: ₦4,153.05.₦3,737.80Current price is: ₦3,737.80. Add to basket Quick View -
SaleAzelto 100 mgNaftidrofuryl oxalate is used to treat peripheral vascular disorders (blood circulation problems outside the brain and heart). It is used to treat the following symptoms of these disorders: Intermittent claudication Cramps in legs at night Severe pain in legs while resting (rest pain) ... Read moreNaftidrofuryl oxalate is used to treat peripheral vascular disorders (blood circulation problems outside the brain and heart). It is used to treat the following symptoms of these disorders: Intermittent claudication Cramps in legs at night Severe pain in legs while resting (rest pain) Pale or blue fngers or toes which get worse when it is cold Numbness, tingling or burning feelings in fngers or toes (Raynaud?s syndrome or acrocyanosis) Open sores on the legs or feet (trophic ulcers) Poor circulation caused by diabetes (diabetic arteriopathy) To treat gangrene Dosage of Azelto 100 mgOne or two Naftidrofuryl oxalate capsules three times daily during meals for a minimum of three months or at the discretion of the physician.ContraindicationsHypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients. Patients with a history of hyperoxaluria or recurrent calcium-containing kidney stones.Side Effects of Azelto 100 mg Gastrointestinal disorders (uncommon): Diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting and epigastric pain. Renal and urinary disorders (very rare): Calcium oxalate kidney stones. Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders (uncommon): Skin rash. Hepatobiliary disorders (rare): Liver damage. Precautions & WarningsThe administration of Azelto 100 mg may modify the composition of the urine, promoting the formation of calcium oxalate kidney stones. The administration of Azelto 100 mg without liquid before going to bed may cause local oesophagitis. Therefore, it is essential to always take the capsule with a sufficient amount of water. Cases of liver damage have been reported.Overdose Effects of Azelto 100 mgDepression of cardiac conduction and convulsions may occur.Storage ConditionsStore below 25?C. Protect from light & moisture. Keep the medicine out of reach of children.Drug Classes5-HT AgonistsMode Of ActionNaftidrofuryl oxalate possesses a 5HT2-blocking activity and counteracts both the vasoconstrictor effect and the effect promoting platelet aggregation due to serotonin. Naftidrofuryl oxalate has a direct effect on intracellular metabolism. Thus it increases ATP level, decreases lactic acid level in ischemic conditions and enhances the cellular oxidative capacity. Also, Naftidrofuryl oxalate is a powerful spasmolytic agent.PregnancyIn the absence of any relevant clinical data, the use of Azelto 100 mg is not advisable during pregnancy. In the absence of specific data concerning the excretion of the drug in human milk, Azelto 100 mg should not be used by breastfeeding women.Sku: 1736101273-2641
Azelto100 mg
₦5,280.00Original price was: ₦5,280.00.₦4,752.00Current price is: ₦4,752.00.₦5,280.00Original price was: ₦5,280.00.₦4,752.00Current price is: ₦4,752.00. Add to basket Quick View -
SaleAzin 500 mgAzin 500 mg is prescribed for infections (produced by susceptible organisms) in the upper respiratory tract, including sinusitis and pharyngitis/tonsillitis, the lower respiratory tract, including bronchitis and pneumonia, the otitis media, and the skin and soft tissue. Azin 500 mg is recommended for the treatment of non-gonococcal urethritis and cervicitis caused by Chlamydia trachomatis in sexually transmitted illnesses in both men and women.Theropeutic ClassMacrolidesPharmacologyAzin 500 mg belongs to the macrolide subclass of antibiotics known as azalide. In order to prevent microbial protein synthesis, Azin 500 mg binds to the 50s ribosomal subunit of susceptible species. Moraxella catarrhalis, anaerobes such as Bacteroides fragilis, Escherichia coli, Bordetella pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis, Borrelia burgdorferi, Haemophilus ducreyi, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae, as well as gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, Streptoc Moreover, in vitro testing of Azin 500 mg shown action against Campylobacter sp., Toxoplasma gondii, Treponema pallidum, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Legionella pneumophila, and hominins.Dosage of Azin 500 mgAdult: 500 mg once daily orally for 3 days or 500 mg once on day 1, then 250 mg once on days 2-5 for 4 days. For sexually transmitted diseases caused by Chlamydia trachomatis in adults, the dose is 1 gm given as a single dose or 500 mg once on day 1, followed by 250 mg once daily for next 2 days may also be given. Children: 10 mg/kg body weight once daily for 3 days for child over 6 months 200 mg (1 teaspoonful) for 3 days if body weight is 15-25 kg 300 mg (1? teaspoonfuls) for 3 days if body weight is 26-35 kg; 400 mg (2 teaspoonfuls) for 3 days if body weight is 36-45 kg. In typhoid fever, 500 mg (21/2 teaspoonfuls) once daily for 7-10 days is given.Administration of Azin 500 mgProcedure for reinstatement after suspension- Step 1: Thoroughly shake the bottle to break up the powder. Step 2: Fill the bottle with boiled and cooled water to the watermark on the label. Step 3: Mix the powder and water thoroughly to combine. Take Azin 500 mg at least one hour before or two hours after eating.Interaction of Azin 500 mgWhen food and antacids are present, Azin 500 mg absorption is lessened. Due to the potential for ergotism brought on by an interaction between Azin 500 mg and the cytochrome P-450 system, Azin 500 mg should be avoided in patients who are receiving ergot alkaloids. With co-administration, care should be taken since macrolides raise the plasma levels of cyclosporin and digoxin. Warfarin, Theophylline, Carbamazepine, Methylprednisolone, or Cimetidine have not been found to interact with Azin 500 mg.ContraindicationsThose who are hypersensitive to Azin 500 mg or any other macrolide antibiotic should not take Azin 500 mg. Ergot derivatives and Azin 500 mg should not be administered together. Those with liver disorders should not use Azin 500 mg.Side Effects of Azin 500 mgLow-frequency side effects are experienced after taking Azin 500 mg. A therapeutic withdrawal will reverse the adverse effects, which include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain or cramps, flatulence, diarrhea, headaches, and skin rashes.Pregnancy & LactationThe Azin 500 mg pregnancy category is B. Studies on animal reproduction have shown that Azin 500 mg has no evidence of harming the fetus. Pregnant women have not been the subject of any good, controlled studies. Azin 500 mg should only be used during pregnancy if no other suitable options are available, as research on animal reproduction are not always indicative of human response. The presence of Azin 500 mg in breast milk is unknown. Hence, when giving Azin 500 mg to nursing mothers, care should be taken.Precautions & WarningsIt is advised to keep an eye out for any superinfection with non-susceptible organisms, such as fungus when using any antibiotic. Those with renal impairment don't require a dose adjustment.Overdose Effects of Azin 500 mgThere is no information on Azin 500 mg overdosage. Macrolide antibiotic overdose symptoms can include hearing loss, extreme nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. The use of gastric lavage and other supportive treatments is advised.Storage ConditionsKeep dry and away from heat and light. Keep out of children's reach.Sku: 1736102344-2952
Azin500 mg
₦3,025.00Original price was: ₦3,025.00.₦2,722.50Current price is: ₦2,722.50.₦3,025.00Original price was: ₦3,025.00.₦2,722.50Current price is: ₦2,722.50. Add to basket Quick View -
SaleAzirox 500 mgAzirox 500 mg is prescribed for infections (produced by susceptible organisms) in the upper respiratory tract, including sinusitis and pharyngitis/tonsillitis, the lower respiratory tract, including bronchitis and pneumonia, the otitis media, and the skin and soft tissue. Azirox 500 mg is recommended for the treatment of non-gonococcal urethritis and cervicitis caused by Chlamydia trachomatis in sexually transmitted illnesses in both men and women.Theropeutic ClassMacrolidesPharmacologyAzirox 500 mg belongs to the macrolide subclass of antibiotics known as azalide. In order to prevent microbial protein synthesis, Azirox 500 mg binds to the 50s ribosomal subunit of susceptible species. Moraxella catarrhalis, anaerobes such as Bacteroides fragilis, Escherichia coli, Bordetella pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis, Borrelia burgdorferi, Haemophilus ducreyi, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae, as well as gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, Streptoc Moreover, in vitro testing of Azirox 500 mg shown action against Campylobacter sp., Toxoplasma gondii, Treponema pallidum, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Legionella pneumophila, and hominins.Dosage of Azirox 500 mgAdult: 500 mg once daily orally for 3 days or 500 mg once on day 1, then 250 mg once on days 2-5 for 4 days. For sexually transmitted diseases caused by Chlamydia trachomatis in adults, the dose is 1 gm given as a single dose or 500 mg once on day 1, followed by 250 mg once daily for next 2 days may also be given. Children: 10 mg/kg body weight once daily for 3 days for child over 6 months 200 mg (1 teaspoonful) for 3 days if body weight is 15-25 kg 300 mg (1? teaspoonfuls) for 3 days if body weight is 26-35 kg; 400 mg (2 teaspoonfuls) for 3 days if body weight is 36-45 kg. In typhoid fever, 500 mg (21/2 teaspoonfuls) once daily for 7-10 days is given.Administration of Azirox 500 mgProcedure for reinstatement after suspension- Step 1: Thoroughly shake the bottle to break up the powder. Step 2: Fill the bottle with boiled and cooled water to the watermark on the label. Step 3: Mix the powder and water thoroughly to combine. Take Azirox 500 mg at least one hour before or two hours after eating.Interaction of Azirox 500 mgWhen food and antacids are present, Azirox 500 mg absorption is lessened. Due to the potential for ergotism brought on by an interaction between Azirox 500 mg and the cytochrome P-450 system, Azirox 500 mg should be avoided in patients who are receiving ergot alkaloids. With co-administration, care should be taken since macrolides raise the plasma levels of cyclosporin and digoxin. Warfarin, Theophylline, Carbamazepine, Methylprednisolone, or Cimetidine have not been found to interact with Azirox 500 mg.ContraindicationsThose who are hypersensitive to Azirox 500 mg or any other macrolide antibiotic should not take Azirox 500 mg. Ergot derivatives and Azirox 500 mg should not be administered together. Those with liver disorders should not use Azirox 500 mg.Side Effects of Azirox 500 mgLow-frequency side effects are experienced after taking Azirox 500 mg. A therapeutic withdrawal will reverse the adverse effects, which include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain or cramps, flatulence, diarrhea, headaches, and skin rashes.Pregnancy & LactationThe Azirox 500 mg pregnancy category is B. Studies on animal reproduction have shown that Azirox 500 mg has no evidence of harming the fetus. Pregnant women have not been the subject of any good, controlled studies. Azirox 500 mg should only be used during pregnancy if no other suitable options are available, as research on animal reproduction are not always indicative of human response. The presence of Azirox 500 mg in breast milk is unknown. Hence, when giving Azirox 500 mg to nursing mothers, care should be taken.Precautions & WarningsIt is advised to keep an eye out for any superinfection with non-susceptible organisms, such as fungus when using any antibiotic. Those with renal impairment don't require a dose adjustment.Overdose Effects of Azirox 500 mgThere is no information on Azirox 500 mg overdosage. Macrolide antibiotic overdose symptoms can include hearing loss, extreme nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. The use of gastric lavage and other supportive treatments is advised.Storage ConditionsKeep dry and away from heat and light. Keep out of children's reach.Sku: 1736097415-1494
Azirox500 mg
₦1,931.05Original price was: ₦1,931.05.₦1,738.00Current price is: ₦1,738.00.₦1,931.05Original price was: ₦1,931.05.₦1,738.00Current price is: ₦1,738.00. Add to basket Quick View -
SaleAzisan Plus 40 mg+12.5 mgFor the treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure: In patients not adequately controlled with ARB monotherapy As initial therapy in patients likely to need multiple drugs to help To achieve blood pressure goals and to reduce the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions.Theropeutic ClassCombined antihypertensive preparationsPharmacologyAzilsartan medoxomil is an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB). Azilsartan helps blood vessels to dilate. It also helps to excrete of Sodium and water from body. This combination also contains a diuretic. Chlorthalidone works in the kidneys to flush excess water and salt (sodium) from the body. Together, these 2 medicines work to help lower blood pressure in people who need more than 1 medicine to treat their high blood pressure (hypertension).Dosage & Administration of Azisan Plus 40 mg+12.5 mgThe recommended starting dose is 40/12.5 mg taken orally once daily. Most of the antihypertensive effect is apparent within 1 to 2 weeks. This combination may be used to provide additional blood pressure lowering for patients not adequately controlled on ARB or diuretic monotherapy treatment. Patients not controlled with azilsartan medoxomil 80 mg may have an additional systolic/diastolic clinic blood pressure reduction of 13/6 mm Hg when switched to this combination 40/12.5 mg.This combination may be used as initial therapy if a patient is likely to need multiple drugs to achieve blood pressure goals. Patients titrated to the individual components (azilsartan medoxomil and chlorthalidone) may instead receive the corresponding dose of This combination.Dosage of Azisan Plus 40 mg+12.5 mgThe recommended starting dose is 40/12.5 mg taken orally once daily. Most of the antihypertensive effect is apparent within 1 to 2 weeks. This combination may be used to provide additional blood pressure lowering for patients not adequately controlled on ARB or diuretic monotherapy treatment. Patients not controlled with azilsartan medoxomil 80 mg may have an additional systolic/diastolic clinic blood pressure reduction of 13/6 mm Hg when switched to this combination 40/12.5 mg.This combination may be used as initial therapy if a patient is likely to need multiple drugs to achieve blood pressure goals. Patients titrated to the individual components (azilsartan medoxomil and chlorthalidone) may instead receive the corresponding dose of this combination. This may be taken with or without food.Interaction of Azisan Plus 40 mg+12.5 mgRenal clearance of lithium is reduced by diuretics, such as chlorthalidone increasing the risk of lithium toxicity. NSAIDs increase risk of renal dysfunction and interfere with antihypertensive effectContraindicationsThis is contraindicated in patients with anuria.Side Effects of Azisan Plus 40 mg+12.5 mgThe following potential adverse reactions are- Fetal toxicity Hypotension in Volume- or Salt-Depleted Patients Impaired Renal Function Hypokalemia Hyperuricemia Pregnancy & LactationPregnancy Category D. Use of drugs that affect the renin-angiotensin system during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy reduces fetal renal function and increases fetal and neonatal morbidity and death.Precautions & Warnings In patients with an activated renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), such as volume- and/or salt-depleted patients, this combination can cause excessive hypotension. Correct volume or salt depletion prior to administration of azilsartan and chlorthalidone. In patients with renal artery stenosis, This combination may cause renal failure. Monitor renal function in patients with renal impairment. Consider discontinuing this combination with progressive renal impairment. Heart rhythm problems (e.g., bradycardia, QT prolongation, ventricular tachycardia), liver problems, certain uncorrected mineral imbalances (low potassium/magnesium levels), severe kidney problems. Storage ConditionsStore in a cool & dry place, away from light and children.Drug ClassesCombined antihypertensive preparationsMode Of ActionAzilsartan medoxomil is an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB). Azilsartan helps blood vessels to dilate. It also helps to excrete of Sodium and water from body. This combination also contains a diuretic. Chlorthalidone works in the kidneys to flush excess water and salt (sodium) from the body. Together, these 2 medicines work to help lower blood pressure in people who need more than 1 medicine to treat their high blood pressure (hypertension).Absorption: Azilsartan medoxomil is rapidly hydrolyzed to azilsartan, the active metabolite, in the gastrointestinal tract during absorption. Azilsartan medoxomil is not detected in plasma after oral administration. The estimated absolute bioavailability of azilsartan following administration of azilsartan medoxomil is approximately 60%. After oral administration of azilsartan medoxomil, peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) of azilsartan are reached within 1.5 to 3 hours. Food does not affect the bioavailability of azilsartan.Distribution: The volume of distribution of azilsartan is approximately 16L. Azilsartan is highly bound to human plasma proteins (>99%), mainly serum albumin. Protein binding is constant at azilsartan plasma concentrations well above the range achieved with recommended doses. In whole blood, chlorthalidone is predominantly bound to erythrocyte carbonic anhydrase. In the plasma, approximately 75% of chlorthalidone is bound to plasma proteins, 58% of the drug being bound to albumin.Metabolism and Elimination: Azilsartan medoxomil: Azilsartan is metabolized to two primary metabolites. The major metabolite in plasma is formed by O-dealkylation, referred to as metabolite M II, and the minor metabolite is formed by decarboxylation, referred to as metabolite M-I. Systemic exposures to the major and minor metabolites in humans were approximately 50% and less than 1% of azilsartan, respectively. M-I and MII do not contribute to the pharmacologic activity of azilsartan medoxomil. The major enzyme responsible for azilsartan metabolism is CYP2C9. The elimination half-life of azilsartan is approximately 11 hours and renal clearance is approximately 2.3 mL/min. Steady-state levels of azilsartan are achieved within 5 days and no accumulation in plasma occurs with repeated once-daily dosing.Chlorthalidone: The major portion of the drug is excreted unchanged by the kidneys. Nonrenal routes of elimination have yet to be clarified. Data are not available regarding the percentage of dose as unchanged drug and metabolites, the concentration of the drug in body fuids, degree of uptake by a particular organ or in the fetus, or passage across the blood-brain barrier.PregnancyPregnancy Category D. Use of drugs that affect the renin-angiotensin system during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy reduces fetal renal function and increases fetal and neonatal morbidity and death.Sku: 1736102445-2982
Azisan Plus40 mg+12.5 mg
₦12,100.00Original price was: ₦12,100.00.₦10,890.00Current price is: ₦10,890.00.₦12,100.00Original price was: ₦12,100.00.₦10,890.00Current price is: ₦10,890.00. Add to basket Quick View -
SaleAzisan 40 mgAzisan 40 mg is indicated for the treatment of hypertension to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily stroke and myocardial infarction. Azisan 40 mg may be used either alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents.Theropeutic ClassAngiotensin-ll receptor blockerPharmacologyAzisan 40 mg, a prodrug, is hydrolyzed to Azilsartan in the gastrointestinal tract during absorption. Azilsartan is a selective AT1 subtype angiotensin II receptor antagonist. Azilsartan blocks the vasoconstrictor and aldosterone secreting effects of angiotensin II by selectively blocking the binding of angiotensin II to the AT1 receptor in many tissues, such as vascular smooth muscle and the adrenal gland.Dosage & Administration of Azisan 40 mgThe recommended dose in adults is 80 mg taken orally once daily. Consider a Starting dose of 40 mg for patients who are treated with high doses of diuretics. If blood pressure is not controlled with Azilsartan alone, additional blood pressure reduction can be achieved by taking Azilsartan with other antihypertensive agents.Dosage of Azisan 40 mgThe recommended dose in adults is 80 mg taken orally once daily. Consider a Starting dose of 40 mg for patients who are treated with high doses of diuretics. If blood pressure is not controlled with Azilsartan alone, additional blood pressure reduction can be achieved by taking Azilsartan with other antihypertensive agents.Interaction of Azisan 40 mgNo drug interactions have been observed in studies of Azisan 40 mg or Azilsartan given with amlodipine, antacids, chlorthalidone, digoxin, fluconazole, glyburide, ketoconazole, metformin, pioglitazone and warfarin. The antihypertensive effect of Azilsartan may be attenuated by the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs including selective COX-2 inhibitors. Dual blockade of the RAS with angiotensin receptor blockers, ACE inhibitors or aliskiren is associated with increased risks of hypotension, hyperkalemia and changes in renal function.ContraindicationsIt is contraindicated to co-administer Aliskiren with Azilsartan in patients with Diabetes.Side Effects of Azisan 40 mgThe most common adverse reaction in adults is diarrhea. The other side effects are nausea, asthenia, fatigue, muscle spasm, dizziness and cough.Pregnancy & LactationPregnancy Category D. The risk to the fetus increases if Azisan 40 mg is administered during the second or third trimesters of pregnancy. It is not known whether Azisan 40 mg is excreted in human milk, as many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for adverse effects on the nursing infant, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.Precautions & WarningsUse of Azisan 40 mg during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy reduces fetal renal function and increases fetal and neonatal morbidity and death. In patients who are intravascularly volume-depleted (e.g., those treated with high-dose diuretics), symptomatic hypotension may occur. Changes in renal function including renal failure has been reported in renal impaired patient.Overdose Effects of Azisan 40 mgLimited data are available related to overdose in humans. In the event of and overdose, supportive therapy should be instituted as dictated by the patient?s clinical status. Azilsartan is not dialyzable.Storage Conditionskeep in a dry place away from light and heat. Keep out of the reach of children.Use In Special PopulationsSafety and effectiveness in pediatric patients under 18 years of ages have not been established.Drug ClassesAngiotensin-ll receptor blockerMode Of ActionAngiotensin II is formed from angiotensin I in a reaction catalyzed by angiotensin-converting enzymes (ACE, kinase II). Angiotensin II is the principal pressor agent of the renin-angiotensin system, with efects that include vasoconstriction, stimulation of synthesis and release of aldosterone, cardiac stimulation, and renal reabsorption of sodium. Azilsartan blocks the vasoconstrictor and aldosteronesecreting efects of angiotensin II by selectively blocking the binding of angiotensin II to the AT1 receptor in many tissues, such as vascular smooth muscle and the adrenal gland. Its action is, therefore, independent of the pathway for angiotensin II synthesis. An AT2 receptor is also found in many tissues, but this receptor is not known to be associated with cardiovascular homeostasis. Azilsartan has more than a 10,000-fold greater afnity for the AT1 receptor than for the AT2 receptor.Blockade of the renin-angiotensin system with ACE inhibitors, which inhibit the biosynthesis of angiotensin II from angiotensin I, is widely used in the treatment of hypertension. ACE inhibitors also inhibit the degradation of bradykinin, a reaction catalyzed by ACE. Because azilsartan does not inhibit ACE (kinase II), it should not afect bradykinin levels. Whether this diference has clinical relevance is not yet known. Azilsartan does not bind to or block other receptors or ion channels known to be important in cardiovascular regulation. Blockade of the angiotensin II receptor inhibits the negative regulatory feedback of angiotensin II on renin secretion, but the resulting increased plasma renin activity and angiotensin II circulating levels do not overcome the efect of azilsartan on blood pressure.Azilsartan inhibits the pressor efects of an angiotensin II infusion in a dose-related manner. An azilsartan single dose equivalent to 32 mg Azisan 40 mg inhibited the maximal pressor efect by approximately 90% at peak, and approximately 60% at 24 hours. Plasma angiotensin I and II concentrations and plasma renin activity increased while plasma aldosterone concentrations decreased after single and repeated administration of Azilsartan to healthy subjects; no clinically signifcant efects on serum potassium or sodium were observed.Absorption: Azilsartan medoxomil is hydrolyzed to azilsartan, the active metabolite, in the gastrointestinal tract during absorption. Azilsartan medoxomil is not detected in plasma after oral administration. Dose proportionality in exposure was established for azilsartan in the Azisan 40 mg dose range of 20 mg to 320 mg after single or multiple dosing. The estimated absolute bioavailability of azilsartan following administration of Azisan 40 mg is approximately 60%. After oral administration of Azisan 40 mg, peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) of azilsartan are reached within 1.5 to 3 hours. Food does not afect the bioavailability of azilsartan.Distribution: The volume of distribution of azilsartan is approximately 16L. Azilsartan is highly bound to human plasma proteins (>99%), mainly serum albumin. Protein binding is constant at azilsartan plasma concentrations well above the range achieved with recommended doses. In rats, minimal azilsartan-associated radioactivity crossed the blood-brain barrier. Azilsartan passed across the placental barrier in pregnant rats and was distributed to the fetus.Metabolism and Elimination: Azilsartan is metabolized to two primary metabolites. The major metabolite in plasma is formed by O-dealkylation, referred to as metabolite M-II, and the minor metabolite is formed by decarboxylation, referred to as metabolite M-I. Systemic exposures to the major and minor metabolites in humans were approximately 50% and less than 1% of azilsartan, respectively. M-I and M-II do not contribute to the pharmacologic activity of Azilsartan. The major enzyme responsible for azilsartan metabolism is CYP2C9.PregnancyPregnancy Category D. The risk to the fetus increases if Azisan 40 mg is administered during the second or third trimesters of pregnancy. It is not known whether Azisan 40 mg is excreted in human milk, as many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for adverse effects on the nursing infant, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.Pediatric UsesPediatric Use: Neonates with a history of in utero exposure to azilsartan. If oliguria or hypotension occurs, support blood pressure and renal function. Exchange transfusions or dialysis may be required. Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients under 18 years of age have not been established.Geriatric Use: No dose adjustment with Azilsartan is necessary in elderly patients. Of the total patients in clinical studies with Azilsartan, 26% were elderly (65 years of age and older); 5% were 75 years of age and older. Abnormally high serum creatinine values were more likely to be reported for patients age 75 year or older. No other differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between elderly patients and younger patients, but the greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.Renal Impairment: Dose adjustment is not required in patients with mild-to-severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease. Patients with moderate to severe renal impairment are more likely to report abnormally high serum creatinine values.Hepatic Impairment: No dose adjustment is necessary for subjects with mild or moderate hepatic impairment. Azilsartan has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment.Sku: 1736106566-4186
Azisan40 mg
₦6,600.00Original price was: ₦6,600.00.₦5,940.00Current price is: ₦5,940.00.₦6,600.00Original price was: ₦6,600.00.₦5,940.00Current price is: ₦5,940.00. Add to basket Quick View -
SaleAzisan 80 mgAzisan 80 mg is indicated for the treatment of hypertension to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily stroke and myocardial infarction. Azisan 80 mg may be used either alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents.Theropeutic ClassAngiotensin-ll receptor blockerPharmacologyAzisan 80 mg, a prodrug, is hydrolyzed to Azilsartan in the gastrointestinal tract during absorption. Azilsartan is a selective AT1 subtype angiotensin II receptor antagonist. Azilsartan blocks the vasoconstrictor and aldosterone secreting effects of angiotensin II by selectively blocking the binding of angiotensin II to the AT1 receptor in many tissues, such as vascular smooth muscle and the adrenal gland.Dosage & Administration of Azisan 80 mgThe recommended dose in adults is 80 mg taken orally once daily. Consider a Starting dose of 40 mg for patients who are treated with high doses of diuretics. If blood pressure is not controlled with Azilsartan alone, additional blood pressure reduction can be achieved by taking Azilsartan with other antihypertensive agents.Dosage of Azisan 80 mgThe recommended dose in adults is 80 mg taken orally once daily. Consider a Starting dose of 40 mg for patients who are treated with high doses of diuretics. If blood pressure is not controlled with Azilsartan alone, additional blood pressure reduction can be achieved by taking Azilsartan with other antihypertensive agents.Interaction of Azisan 80 mgNo drug interactions have been observed in studies of Azisan 80 mg or Azilsartan given with amlodipine, antacids, chlorthalidone, digoxin, fluconazole, glyburide, ketoconazole, metformin, pioglitazone and warfarin. The antihypertensive effect of Azilsartan may be attenuated by the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs including selective COX-2 inhibitors. Dual blockade of the RAS with angiotensin receptor blockers, ACE inhibitors or aliskiren is associated with increased risks of hypotension, hyperkalemia and changes in renal function.ContraindicationsIt is contraindicated to co-administer Aliskiren with Azilsartan in patients with Diabetes.Side Effects of Azisan 80 mgThe most common adverse reaction in adults is diarrhea. The other side effects are nausea, asthenia, fatigue, muscle spasm, dizziness and cough.Pregnancy & LactationPregnancy Category D. The risk to the fetus increases if Azisan 80 mg is administered during the second or third trimesters of pregnancy. It is not known whether Azisan 80 mg is excreted in human milk, as many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for adverse effects on the nursing infant, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.Precautions & WarningsUse of Azisan 80 mg during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy reduces fetal renal function and increases fetal and neonatal morbidity and death. In patients who are intravascularly volume-depleted (e.g., those treated with high-dose diuretics), symptomatic hypotension may occur. Changes in renal function including renal failure has been reported in renal impaired patient.Overdose Effects of Azisan 80 mgLimited data are available related to overdose in humans. In the event of and overdose, supportive therapy should be instituted as dictated by the patient?s clinical status. Azilsartan is not dialyzable.Storage Conditionskeep in a dry place away from light and heat. Keep out of the reach of children.Use In Special PopulationsSafety and effectiveness in pediatric patients under 18 years of ages have not been established.Drug ClassesAngiotensin-ll receptor blockerMode Of ActionAngiotensin II is formed from angiotensin I in a reaction catalyzed by angiotensin-converting enzymes (ACE, kinase II). Angiotensin II is the principal pressor agent of the renin-angiotensin system, with efects that include vasoconstriction, stimulation of synthesis and release of aldosterone, cardiac stimulation, and renal reabsorption of sodium. Azilsartan blocks the vasoconstrictor and aldosteronesecreting efects of angiotensin II by selectively blocking the binding of angiotensin II to the AT1 receptor in many tissues, such as vascular smooth muscle and the adrenal gland. Its action is, therefore, independent of the pathway for angiotensin II synthesis. An AT2 receptor is also found in many tissues, but this receptor is not known to be associated with cardiovascular homeostasis. Azilsartan has more than a 10,000-fold greater afnity for the AT1 receptor than for the AT2 receptor.Blockade of the renin-angiotensin system with ACE inhibitors, which inhibit the biosynthesis of angiotensin II from angiotensin I, is widely used in the treatment of hypertension. ACE inhibitors also inhibit the degradation of bradykinin, a reaction catalyzed by ACE. Because azilsartan does not inhibit ACE (kinase II), it should not afect bradykinin levels. Whether this diference has clinical relevance is not yet known. Azilsartan does not bind to or block other receptors or ion channels known to be important in cardiovascular regulation. Blockade of the angiotensin II receptor inhibits the negative regulatory feedback of angiotensin II on renin secretion, but the resulting increased plasma renin activity and angiotensin II circulating levels do not overcome the efect of azilsartan on blood pressure.Azilsartan inhibits the pressor efects of an angiotensin II infusion in a dose-related manner. An azilsartan single dose equivalent to 32 mg Azisan 80 mg inhibited the maximal pressor efect by approximately 90% at peak, and approximately 60% at 24 hours. Plasma angiotensin I and II concentrations and plasma renin activity increased while plasma aldosterone concentrations decreased after single and repeated administration of Azilsartan to healthy subjects; no clinically signifcant efects on serum potassium or sodium were observed.Absorption: Azilsartan medoxomil is hydrolyzed to azilsartan, the active metabolite, in the gastrointestinal tract during absorption. Azilsartan medoxomil is not detected in plasma after oral administration. Dose proportionality in exposure was established for azilsartan in the Azisan 80 mg dose range of 20 mg to 320 mg after single or multiple dosing. The estimated absolute bioavailability of azilsartan following administration of Azisan 80 mg is approximately 60%. After oral administration of Azisan 80 mg, peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) of azilsartan are reached within 1.5 to 3 hours. Food does not afect the bioavailability of azilsartan.Distribution: The volume of distribution of azilsartan is approximately 16L. Azilsartan is highly bound to human plasma proteins (>99%), mainly serum albumin. Protein binding is constant at azilsartan plasma concentrations well above the range achieved with recommended doses. In rats, minimal azilsartan-associated radioactivity crossed the blood-brain barrier. Azilsartan passed across the placental barrier in pregnant rats and was distributed to the fetus.Metabolism and Elimination: Azilsartan is metabolized to two primary metabolites. The major metabolite in plasma is formed by O-dealkylation, referred to as metabolite M-II, and the minor metabolite is formed by decarboxylation, referred to as metabolite M-I. Systemic exposures to the major and minor metabolites in humans were approximately 50% and less than 1% of azilsartan, respectively. M-I and M-II do not contribute to the pharmacologic activity of Azilsartan. The major enzyme responsible for azilsartan metabolism is CYP2C9.PregnancyPregnancy Category D. The risk to the fetus increases if Azisan 80 mg is administered during the second or third trimesters of pregnancy. It is not known whether Azisan 80 mg is excreted in human milk, as many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for adverse effects on the nursing infant, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.Pediatric UsesPediatric Use: Neonates with a history of in utero exposure to azilsartan. If oliguria or hypotension occurs, support blood pressure and renal function. Exchange transfusions or dialysis may be required. Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients under 18 years of age have not been established.Geriatric Use: No dose adjustment with Azilsartan is necessary in elderly patients. Of the total patients in clinical studies with Azilsartan, 26% were elderly (65 years of age and older); 5% were 75 years of age and older. Abnormally high serum creatinine values were more likely to be reported for patients age 75 year or older. No other differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between elderly patients and younger patients, but the greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.Renal Impairment: Dose adjustment is not required in patients with mild-to-severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease. Patients with moderate to severe renal impairment are more likely to report abnormally high serum creatinine values.Hepatic Impairment: No dose adjustment is necessary for subjects with mild or moderate hepatic impairment. Azilsartan has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment.Sku: 1736101355-2666
Azisan80 mg
₦12,100.00Original price was: ₦12,100.00.₦10,890.00Current price is: ₦10,890.00.₦12,100.00Original price was: ₦12,100.00.₦10,890.00Current price is: ₦10,890.00. Add to basket Quick View -
SaleAzithrocin 200 mg/5 mlAzithromycin is indicated for infections (caused by susceptible organisms) in lower respiratory tract infections including bronchitis and pneumonia, in upper respiratory tract infections including sinusitis and pharyngitis/tonsillitis, in otitis media, and in skin and soft tissue infections. In sexually ... Read moreAzithromycin is indicated for infections (caused by susceptible organisms) in lower respiratory tract infections including bronchitis and pneumonia, in upper respiratory tract infections including sinusitis and pharyngitis/tonsillitis, in otitis media, and in skin and soft tissue infections. In sexually transmitted diseases in men and women, Azithromycin?is indicated in the treatment of non-gonococcal urethritis and cervicitis due to Chlamydia trachomatis.Dosage of Azithrocin 200 mg/5 mlOral-Adult: 500 mg once daily orally for 3 days or 500 mg once on day 1, then 250 mg once on days 2-5 for 4 days. For sexually transmitted diseases caused by Chlamydia trachomatis in adults, the dose is 1 gm given as a single dose or 500 mg once on day 1, followed by 250 mg once daily for next 2 days may also be given.Children: 10 mg/kg body weight once daily for 3 days for child over 6 months 200 mg (1 teaspoonful) for 3 days if body weight is 15-25 kg 300 mg (1? teaspoonfuls) for 3 days if body weight is 26-35 kg; 400 mg (2 teaspoonfuls) for 3 days if body weight is 36-45 kg. In typhoid fever, 500 mg (2? teaspoonfuls) once daily for 7-10 days is given. Azithromycin Injection (For IV Infusion only): The recommended dose of Azithromycin for injection for the treatment of adult patients with community-acquired pneumonia due to the indicated organisms is: 500 mg as a single daily dose by the intravenous route for at least two days. Intravenous therapy should be followed by Azithromycin by the oral route at a single, daily dose of 500 mg, administered as two 250-mg tablets to complete a 7 to 10-day course of therapy. The timing of the switch to oral therapy should be done at the discretion of the physician and in accordance with clinical response. The recommended dose of Azithromycin for the treatment of adult patients with pelvic inflammatory disease due to the indicated organisms is: 500 mg as a single daily dose by the intravenous route for one or two days. Intravenous therapy should be followed by Azithromycin by the oral route at a single, daily dose of 250 mg to complete a 7-day course of therapy. The timing of the switch to oral therapy should be done at the discretion of the physician and in accordance with clinical response. If anaerobic microorganisms are suspected of contributing to the infection, an antimicrobial agent with anaerobic activity should be administered in combination with Azithromycin. Safety and effectiveness of azithromycin for injection in children or adolescents under 16 years have not been established. Administration of Azithrocin 200 mg/5 mlReconstitution procedure of suspension- Step 01: Shake the bottle well to loosen the powder. Step 02: Add boiled and cooled water up to the water mark of the bottle label. Step 03: Shake until powder is completely mixed with water. Azithromycin should be taken at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after meal.Interaction of Azithrocin 200 mg/5 mlAzithromycin absorption is reduced in presence of food and antacid. In patients receiving ergot alkaloids Azithromycin should be avoided because of the possibility of ergotism resulting from interaction of Azithromycin with the cytochrome P-450 system. As macrolides increase the plasma concentration of digoxin and cyclosporin, caution should be exercised while co-administration. There have been no drug interactions between Azithromycin and Warfarin, Theophylline, Carbamazepine, Methylprednisolone or Cimetidine.ContraindicationsAzithromycin is contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to Azithromycin or any other macrolide antibiotic. Co-administration of ergot derivatives and Azithromycin is contraindicated. Azithromycin is contraindicated in patients with hepatic diseases.Side Effects of Azithrocin 200 mg/5 mlAzithromycin is well tolerated with a low incidence of side effects. The side effects include nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort (pain/cramps), flatulence, diarrhoea, headache, dizziness, and skin rashes and are reversible upon discontinuation of therapy.Precautions & WarningsAs with any antibiotic, observation for signs of superinfection with non-susceptible organisms, including fungi, is recommended.Renal impairment patient: No dose adjustment is needed in patients with renal impairment. Hepatic impairment patient: The pharmacokinetics of azithromycin in subjects with hepatic impairment has not been established.Geriatric patient: Pharmacokinetic parameters in older volunteers (65 to 85 years old) were similar to those in young adults (18 to 40 years old) for the 5-day therapeutic regimen. Dosage adjustment does not appear to be necessary for older patients with normal renal and hepatic function receiving treatment with this dosage regimen.Overdose Effects of Azithrocin 200 mg/5 mlThere is no data on overdosage with Azithromycin. Typical symptoms of overdosage with macrolide antibiotics include hearing loss, severe nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea. Gastric lavage and general supportive measures are indicated.Storage ConditionsKeep in a dry place away from light and heat. Keep out of the reach of children.Mode Of ActionAzithromycin is acid-stable and can therefore be taken orally with no need of protection from gastric acids. It is readily absorbed; its absorption is greater on an empty stomach. Time to peak concentration in adults is 2.1 to 3.2 hours for oral dosage forms. Due to the high concentration in phagocytes, azithromycin is actively transported to the site of infection. During active phagocytosis, large concentrations of azithromycin are released. The concentration of azithromycin in the tissues can be over 50 times higher than in plasma. This is due to ion trapping and the high lipid solubility.Azithromycin's half-life allows a large single dose to be administered and yet maintain bacteriostatic levels in the infected tissue for several days. Following a single 500 mg dose, plasma concentrations of azithromycin declined in a polyphasic pattern with a mean apparent plasma clearance of 630 mL/min and a terminal elimination half life of 68 hours. The prolonged terminal half-life is thought to be due to extensive uptake and subsequent release of drug from tissues. Biliary excretion of azithromycin, predominantly unchanged, is a major route of elimination. Over the course of a week, approximately 6% of the administered dose appears as unchanged drug in urine.Microbiology: Azithromycin acts by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit of susceptible microorganisms and, thus, interfering with microbial protein synthesis. Nucleic acid synthesis is not affected. Azithromycin has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following microorganisms, both in vitro and in clinical infections: Aerobic and facultative gram-positive microorganisms: Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes Aerobic and facultative gram-negative microorganisms: Haemophilus ducreyi, Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae Other microorganisms: Chlamydia pneumoniae, Chlamydia trachomatis , Mycoplasma pneumoniae , Betalactamase production should have no effect on azithromycin activity. Aerobic and facultative gram-positive microorganisms: Streptococci (Groups C,F,G), Viridans group streptococci Aerobic and facultative gram-negative microorganisms: Bordetella pertussis, Legionella pneumophila Anaerobic microorganisms: Peptostreptococcus species, Prevotella bivia PregnancyPregnancy Category of Azithromycin is B. Animal reproduction studies have demonstrated that Azithromycin has no evidence of harm to the fetus. There are no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women. Since animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, Azithromycin should be used during pregnancy only if adequate alternatives are not available. It is not known whether Azithromycin is secreted in breast milk. So, caution should be exercised when Azithromycin is administered to nursing women.Sku: 1736093863-542
Azithrocin200 mg/5 ml
₦10,175.00Original price was: ₦10,175.00.₦9,157.50Current price is: ₦9,157.50.₦10,175.00Original price was: ₦10,175.00.₦9,157.50Current price is: ₦9,157.50. Add to basket Quick View -
SaleAzithrocin 500 mgAzithrocin 500 mg is prescribed for infections (produced by susceptible organisms) in the upper respiratory tract, including sinusitis and pharyngitis/tonsillitis, the lower respiratory tract, including bronchitis and pneumonia, the otitis media, and the skin and soft tissue. Azithrocin 500 mg is recommended for the treatment of non-gonococcal urethritis and cervicitis caused by Chlamydia trachomatis in sexually transmitted illnesses in both men and women.Theropeutic ClassMacrolidesPharmacologyAzithrocin 500 mg belongs to the macrolide subclass of antibiotics known as azalide. In order to prevent microbial protein synthesis, Azithrocin 500 mg binds to the 50s ribosomal subunit of susceptible species. Moraxella catarrhalis, anaerobes such as Bacteroides fragilis, Escherichia coli, Bordetella pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis, Borrelia burgdorferi, Haemophilus ducreyi, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae, as well as gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, Streptoc Moreover, in vitro testing of Azithrocin 500 mg shown action against Campylobacter sp., Toxoplasma gondii, Treponema pallidum, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Legionella pneumophila, and hominins.Dosage of Azithrocin 500 mgAdult: 500 mg once daily orally for 3 days or 500 mg once on day 1, then 250 mg once on days 2-5 for 4 days. For sexually transmitted diseases caused by Chlamydia trachomatis in adults, the dose is 1 gm given as a single dose or 500 mg once on day 1, followed by 250 mg once daily for next 2 days may also be given. Children: 10 mg/kg body weight once daily for 3 days for child over 6 months 200 mg (1 teaspoonful) for 3 days if body weight is 15-25 kg 300 mg (1? teaspoonfuls) for 3 days if body weight is 26-35 kg; 400 mg (2 teaspoonfuls) for 3 days if body weight is 36-45 kg. In typhoid fever, 500 mg (21/2 teaspoonfuls) once daily for 7-10 days is given.Administration of Azithrocin 500 mgProcedure for reinstatement after suspension- Step 1: Thoroughly shake the bottle to break up the powder. Step 2: Fill the bottle with boiled and cooled water to the watermark on the label. Step 3: Mix the powder and water thoroughly to combine. Take Azithrocin 500 mg at least one hour before or two hours after eating.Interaction of Azithrocin 500 mgWhen food and antacids are present, Azithrocin 500 mg absorption is lessened. Due to the potential for ergotism brought on by an interaction between Azithrocin 500 mg and the cytochrome P-450 system, Azithrocin 500 mg should be avoided in patients who are receiving ergot alkaloids. With co-administration, care should be taken since macrolides raise the plasma levels of cyclosporin and digoxin. Warfarin, Theophylline, Carbamazepine, Methylprednisolone, or Cimetidine have not been found to interact with Azithrocin 500 mg.ContraindicationsThose who are hypersensitive to Azithrocin 500 mg or any other macrolide antibiotic should not take Azithrocin 500 mg. Ergot derivatives and Azithrocin 500 mg should not be administered together. Those with liver disorders should not use Azithrocin 500 mg.Side Effects of Azithrocin 500 mgLow-frequency side effects are experienced after taking Azithrocin 500 mg. A therapeutic withdrawal will reverse the adverse effects, which include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain or cramps, flatulence, diarrhea, headaches, and skin rashes.Pregnancy & LactationThe Azithrocin 500 mg pregnancy category is B. Studies on animal reproduction have shown that Azithrocin 500 mg has no evidence of harming the fetus. Pregnant women have not been the subject of any good, controlled studies. Azithrocin 500 mg should only be used during pregnancy if no other suitable options are available, as research on animal reproduction are not always indicative of human response. The presence of Azithrocin 500 mg in breast milk is unknown. Hence, when giving Azithrocin 500 mg to nursing mothers, care should be taken.Precautions & WarningsIt is advised to keep an eye out for any superinfection with non-susceptible organisms, such as fungus when using any antibiotic. Those with renal impairment don't require a dose adjustment.Overdose Effects of Azithrocin 500 mgThere is no information on Azithrocin 500 mg overdosage. Macrolide antibiotic overdose symptoms can include hearing loss, extreme nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. The use of gastric lavage and other supportive treatments is advised.Storage ConditionsKeep dry and away from heat and light. Keep out of children's reach.Sku: 1736104695-3630
Azithrocin500 mg
₦1,925.00Original price was: ₦1,925.00.₦1,732.50Current price is: ₦1,732.50.₦1,925.00Original price was: ₦1,925.00.₦1,732.50Current price is: ₦1,732.50. Add to basket Quick View -
SaleAzofend 200 mgAn azole antifungal drug is Azofend 200 mg. The following fungal infections are recommended for use in individuals 12 years of age and older. Aspergillosis invasive Disseminated candidiasis and candidemia (nonneutropenic) in the skin, abdomen, kidney, bladder wall, and wounds Esophageal candidiasis Severe infections brought on by Fusarium species include Fusarium solani Scedosporium apiospermum Those who are resistant to or intolerant of alternative treatments.Theropeutic ClassOther Antifungal preparationsPharmacologyThe major mechanism of action of Azofend 200 mg is the suppression of 14 alpha-lanosterol demethylation, which is mediated by fungal cytochrome P450 and is a crucial step in the manufacture of fungal ergosterol. The buildup of 14 alpha-methyl sterols and subsequent loss of ergosterol from the fungal cell membrane may be what gives Azofend 200 mg its antifungal properties. It has been demonstrated that Azofend 200 mg is more selective for cytochrome P-450 enzymes found in fungi than for other cytochrome P-450 enzyme systems found in mammals.Dosage of Azofend 200 mgOral-Azofend 200 mg tablet and powder for suspension are to be taken at least one hour before or one hour following a meal At or over 40 kg body weight: Loading dose regimen is 400 mg or 10 ml every 12 hours (for the first 24 hours) and maintenance dose (after first 24 hours) is 200 mg or 5 ml twice daily. Below 40 Kg body weight: Loading dose regimen is 200 mg or 5 ml every 12 hours (for the first 24 hours) and maintenance dose (after first 24 hours) is 100 mg or 2.5 ml twice daily. Or, as directed by the registered physician. Injection-Invasive Aspergillosisd : Loading dose: 6 mg/kg 12 hourly for the first 24 hours. Maintenance Dose: 4 mg/kg 12 hourly. Candidemia in nonneutropenic patients and other deep tissue Candida infections: Loading dose: 6 mg/kg 12 hourly for the first 24 hours. Maintenance Dose: 3-4 mg/kg 12 hourly. Scedosporiosis and Fusariosis: Loading dose: 6 mg/kg 12 hourly for the first 24 hours. Maintenance Dose: 4 mg/kg 12 hourly.Administration of Azofend 200 mgIt is recommended to take Azofend 200 mg film-coated pills at least one hour before or one hour after a meal. Depending on the patient's clinical and mycological response, the length of the treatment should be as brief as possible. Azofend 200 mg exposure longer than 180 days (6 months) must be carefully weighed against the risks and benefits. prevention in both adults and children Beginning the day of the transplant, prophylaxis can be given for up to 100 days. Depending on the risk of acquiring invasive fungal infection (IFI), as indicated by neutropenia or immunosuppression, prophylaxis should be as brief as possible. In the event of ongoing immunosuppression or graft against host disease, it may only be continued for up to 180 days following transplantation (GvHD).Interaction of Azofend 200 mgInhibitors and inducers of CYP3A4, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19: Azofend 200 mg dosage should be changed, and side effects or ineffectiveness should be watched for. Drugs that are CYP3A4, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19 substrates may have higher concentrations and activities when taken with Azofend 200 mg. Decrease these other drugs' dosages and keep an eye out for any negative effects Raise the maintenance dose of oral and intravenous Azofend 200 mg when also taking phenytoin or efavirenzContraindicationsKnown sensitivity to the drug's active ingredient, Azofend 200 mg, or any other ingredient- Risk of major adverse effects necessitates avoiding co-administration of sirolimus with terfenadine, astemizole, cisapride, pimozide, or quinidine. Rifampin, carbamazepine, long-acting barbiturates, efavirenz, ritonavir, rifabutin, ergot alkaloids, and St. John's Wort should not be administered together due to the possibility of efficacy loss.Side Effects of Azofend 200 mgAbdominal pain, anemia, impaired vision, headaches, chest pain, nausea, and diarrhea are the most frequent adverse effects.Pregnancy & LactationThere aren't enough facts about Azofend 200 mg use during pregnancy. If the potential risk to the fetus is not clearly outweighed by the benefit to the mother, Azofend 200 mg should not be administered during pregnancy. There hasn't been any research done on Azofend 200 mg excretion into breast milk. Following the start of Azofend 200 mg treatment, breastfeeding must be discontinued.Precautions & WarningsThe benefit-risk balance of long-term exposure (treatment or prophylaxis) of more than 180 days must be carefully weighed. Long-term Azofend 200 mg therapy has been linked to reports of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin (SCC).Overdose Effects of Azofend 200 mgThere is no data found about overdose of Azofend 200 mg.Storage ConditionsKeep out of children's reach. Keep away from light in a dry area with a temperature below 25?C. Azofend 200 mg powder for suspension should be kept between 2? and 8?C.Use In Special PopulationsOlder people do not require a dosage change. Pediatric population: It is unknown whether Azofend 200 mg is safe and effective for use in children under the age of two. Renal impairment: Renal impairment has no impact on the pharmacokinetics of Azofend 200 mg taken orally. As a result, the oral dosage is unaffected in individuals with mild to severe renal impairment. Haemodialysis clearance for Azofend 200 mg is 121 ml/min. Azofend 200 mg is not enough removed by a 4-hour hemodialysate to require a dose change. Hepatic impairment: In patients receiving Azofend 200 mg who have mild to severe hepatic cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A and B), it is advised to utilize the regular loading dosage regimens but to cut the maintenance dose in half. Patients with severe chronic hepatic cirrhosis have not been examined with Azofend 200 mg. In individuals with abnormal liver function tests (aspartate transaminase [AST], alanine transaminase [ALT], alkaline phosphatase [ALP], or total bilirubin >5 times the upper limit of normal), there is minimal information on the safety of Azofend 200 mg. Only use Azofend 200 mg in patients with severe hepatic impairment if the benefit justifies the potential risk because it has been linked to increases in liver function tests and clinical symptoms of liver damage, such as jaundice. Drug toxicity in patients with a severe hepatic impairment needs to be closely watched.Drug ClassesOther Antifungal preparationsMode Of ActionA triazole antifungal drug called Azofend 200 mg is used to treat severe fungi infections. By preventing CYP450-dependent 14-alpha sterol demethylase from functioning, Azofend 200 mg binds and prevents the formation of ergosterol. Ergosterol levels in the membrane of fungal cells decrease as a result of the suppression of 14-alpha sterol demethylase.PregnancyThere is no sufficient, carefully regulated research on pregnant women. Only if the possible benefit outweighs the potential risk to the fetus should it be taken during pregnancy.Pediatric UsesThe effectiveness for children under the age of 12 has not been established.Sku: 1736096370-1194
Azofend200 mg
₦42,900.00Original price was: ₦42,900.00.₦39,468.00Current price is: ₦39,468.00.₦42,900.00Original price was: ₦42,900.00.₦39,468.00Current price is: ₦39,468.00. Add to basket Quick View -
SaleAzomac 500 mgAzomac 500 mg is prescribed for infections (produced by susceptible organisms) in the upper respiratory tract, including sinusitis and pharyngitis/tonsillitis, the lower respiratory tract, including bronchitis and pneumonia, the otitis media, and the skin and soft tissue. Azomac 500 mg is recommended for the treatment of non-gonococcal urethritis and cervicitis caused by Chlamydia trachomatis in sexually transmitted illnesses in both men and women.Theropeutic ClassMacrolidesPharmacologyAzomac 500 mg belongs to the macrolide subclass of antibiotics known as azalide. In order to prevent microbial protein synthesis, Azomac 500 mg binds to the 50s ribosomal subunit of susceptible species. Moraxella catarrhalis, anaerobes such as Bacteroides fragilis, Escherichia coli, Bordetella pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis, Borrelia burgdorferi, Haemophilus ducreyi, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae, as well as gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, Streptoc Moreover, in vitro testing of Azomac 500 mg shown action against Campylobacter sp., Toxoplasma gondii, Treponema pallidum, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Legionella pneumophila, and hominins.Dosage of Azomac 500 mgAdult: 500 mg once daily orally for 3 days or 500 mg once on day 1, then 250 mg once on days 2-5 for 4 days. For sexually transmitted diseases caused by Chlamydia trachomatis in adults, the dose is 1 gm given as a single dose or 500 mg once on day 1, followed by 250 mg once daily for next 2 days may also be given. Children: 10 mg/kg body weight once daily for 3 days for child over 6 months 200 mg (1 teaspoonful) for 3 days if body weight is 15-25 kg 300 mg (1? teaspoonfuls) for 3 days if body weight is 26-35 kg; 400 mg (2 teaspoonfuls) for 3 days if body weight is 36-45 kg. In typhoid fever, 500 mg (21/2 teaspoonfuls) once daily for 7-10 days is given.Administration of Azomac 500 mgProcedure for reinstatement after suspension- Step 1: Thoroughly shake the bottle to break up the powder. Step 2: Fill the bottle with boiled and cooled water to the watermark on the label. Step 3: Mix the powder and water thoroughly to combine. Take Azomac 500 mg at least one hour before or two hours after eating.Interaction of Azomac 500 mgWhen food and antacids are present, Azomac 500 mg absorption is lessened. Due to the potential for ergotism brought on by an interaction between Azomac 500 mg and the cytochrome P-450 system, Azomac 500 mg should be avoided in patients who are receiving ergot alkaloids. With co-administration, care should be taken since macrolides raise the plasma levels of cyclosporin and digoxin. Warfarin, Theophylline, Carbamazepine, Methylprednisolone, or Cimetidine have not been found to interact with Azomac 500 mg.ContraindicationsThose who are hypersensitive to Azomac 500 mg or any other macrolide antibiotic should not take Azomac 500 mg. Ergot derivatives and Azomac 500 mg should not be administered together. Those with liver disorders should not use Azomac 500 mg.Side Effects of Azomac 500 mgLow-frequency side effects are experienced after taking Azomac 500 mg. A therapeutic withdrawal will reverse the adverse effects, which include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain or cramps, flatulence, diarrhea, headaches, and skin rashes.Pregnancy & LactationThe Azomac 500 mg pregnancy category is B. Studies on animal reproduction have shown that Azomac 500 mg has no evidence of harming the fetus. Pregnant women have not been the subject of any good, controlled studies. Azomac 500 mg should only be used during pregnancy if no other suitable options are available, as research on animal reproduction are not always indicative of human response. The presence of Azomac 500 mg in breast milk is unknown. Hence, when giving Azomac 500 mg to nursing mothers, care should be taken.Precautions & WarningsIt is advised to keep an eye out for any superinfection with non-susceptible organisms, such as fungus when using any antibiotic. Those with renal impairment don't require a dose adjustment.Overdose Effects of Azomac 500 mgThere is no information on Azomac 500 mg overdosage. Macrolide antibiotic overdose symptoms can include hearing loss, extreme nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. The use of gastric lavage and other supportive treatments is advised.Storage ConditionsKeep dry and away from heat and light. Keep out of children's reach.Sku: 1736097613-1553
Azomac500 mg
₦1,925.00Original price was: ₦1,925.00.₦1,732.50Current price is: ₦1,732.50.₦1,925.00Original price was: ₦1,925.00.₦1,732.50Current price is: ₦1,732.50. Add to basket Quick View -
SaleAzonox 100 mgAzonox 100 mg is indicated in- Tinea corporis, Tinea cruris, Tinea pedis, Tinea manus, Vulvovaginal candidiasis, Fungal keratitis, Pityriasis versicolor, Oropharyngeal candidiasis, Onychomycosis, Histoplasmosis, Systemic Infections: (Aspergillosis, Candidiasis and Cryptococcus when other drugs are effective) ... Read moreAzonox 100 mg is indicated in- Tinea corporis, Tinea cruris, Tinea pedis, Tinea manus, Vulvovaginal candidiasis, Fungal keratitis, Pityriasis versicolor, Oropharyngeal candidiasis, Onychomycosis, Histoplasmosis, Systemic Infections: (Aspergillosis, Candidiasis and Cryptococcus when other drugs are effective) Antifungal prophylaxis: To prevent systemic fungal infection in severely neutropenic patients. Theropeutic ClassDrugs for subcutaneous and mycosesPharmacologyAzonox 100 mg is an orally active triazole antifungal drug that has demonstrated a broad spectrum of activity and favorable pharmacokinetic profile. Azonox 100 mg inhibits Cytochrome P-450 dependent enzymes resulting in impairment of the biosynthesis of ergosterol, a major component of the cell membrane of yeast and fungal cells. Being integral to the proper functioning of the cell membrane, inhibition of the synthesis of ergosterol leads to a cascade of abnormalities in permeability, membrane bound enzyme activity, and co-ordination of chitin synthesis leading to inhibition of growth, abnormal cell wall formation and accumulation of intracellular lipids and membranous vesicles.Dosage of Azonox 100 mgTinea corporis, Tinea cruris: 100 mg daily for 2 weeks.Tinea pedis, Tinea manus: 100 mg daily for 4 weeks.Vulvovaginal candidiasis: 200 mg twice daily for 1 day or 200 mg daily for 3 days.Fungal keratitis: 200 mg daily for 3 weeks.Pityriasis versicolor: 200 mg daily for 1 week.Oropharyngeal candidiasis: 100 mg daily (200 mg for AIDS patients) for 15 days.Onychomycosis: 200 mg daily for 3 months; or 200 mg twice daily for 7 days (course), subsequent courses repeated after 21 day interval; fingernails 2 courses and toenails 3 courses.Histoplasmosis: 200 mg 1-2 times daily.Systemic Infections: (Aspergillosis, Candidiasis and Cryptococcus when other drugs are effective) 200 mg once daily, increased in invasive or in cryptococcal meningitis to 200 mg twice daily.Antifungal prophylaxis: To prevent systemic fungal infection in severely neutropenic patients: 100mg daily. Or as directed by the physician.Administration of Azonox 100 mgShould be taken with food. Take immediately after a full meal.Interaction of Azonox 100 mgAzonox 100 mg inhibits the metabolism of Cyclosporine and Warfarin. Interaction with Terfenadine, Phenobarbitone, Midazolam has been reported.ContraindicationsThe drug is contraindicated in patients with a known history of hypersensitivity to it. The drug is also contraindicated in pregnant women and patients with known severe hepatic disease. It is also contraindicated with Rifampicin therapy.Side Effects of Azonox 100 mgNausea, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, constipation, headache, dizziness, raised liver enzymes, hepatitis, cholestatic jaundice, peripheral neuropathy have been reported.Pregnancy & LactationAzonox 100 mg is contraindicated in pregnancy. Breast feeding while receiving Azonox 100 mg is not recommended.Precautions & WarningsHepatic enzyme value should be monitored in patients with preexisting hepatic function abnormalities. It should also be done periodically in all patients receiving continuous treatment for more than one month or at any time a patients develops sign and symptoms suggestive liver dysfunction.Overdose Effects of Azonox 100 mgThere is no experience of overdosage with Azonox 100 mg.Storage ConditionsStore below 30?C, away from light & in a dry place. Keep out of the reach of children.Drug ClassesDrugs for subcutaneous and mycosesMode Of ActionAzonox 100 mg is an orally active triazole antifungal agent, having broad-spectrum activity and a favourable pharmacokinetic profile. Azonox 100 mg inhibits cytochrome p-450 dependent enzymes resulting in impairment of the biosynthesis of ergoesterol, a major component of the cell membrane of yeast and fungal cells.PregnancyNot recommended during pregnancy & lactation, unless otherwise indicated by the physician.Pediatric UsesThe efficacy and safety of the Azonox 100 mg capsule have not been established in pediatric patients.Sku: 1736100898-2526
Azonox100 mg
₦825.00Original price was: ₦825.00.₦742.50Current price is: ₦742.50. -
SaleAzopt 2%+0.5%This Eye Drops is indicated for the treatment of elevated intraocular pressure in patients with open angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension who are insufficiently responsive to topical beta blockers.Theropeutic ClassDrugs for miotics and glaucomaPharmacologyDorzolamide, a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, has actions similar to acetazolamide. By inhibiting carbonic anhydrase in the ciliary processes of the eye, dorzolamide decreases aqueous humor secretion. Used together, there is additional intraocular pressure reduction compared to using either component alone, but the reduction is not as much as concomitant admin of dorzolamide tid and timolol bid.Timolol maleate, a nonselective ?-adrenergic blocker, reduces aqueous humor formation.Dosage & Administration of Azopt 2%+0.5%Instill one drop in the conjunctival sac of the affected eye(s) twice daily.Dosage of Azopt 2%+0.5%Instill one drop in the conjunctival sac of the affected eye(s) twice daily.Interaction of Azopt 2%+0.5%Additive hypotension and bradycardia with oral calcium channel blockers, catecholamine-depleting drugs or ?-blockers, antiarrhythmics (e.g. amiodarone), digitalis glycosides, parasympathomimetics, narcotics and MAOIs. Additive systemic side effects with oral carbonic anhydrase or ?-blockers; avoid concurrent use. Additive systemic ?-blockade with CYP2D6 inhibitors (e.g. quinidine, SSRIs) and timolol.ContraindicationsContraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to any of the components of this preparation.Side Effects of Azopt 2%+0.5%Mild burning, ocular hyperemia, blurred vision may occur.Pregnancy & LactationUse in pregnancy: There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. This Eye Drops should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.?Use in lactation: Caution should be exercised when This Eye Drops is administered to a nursing mother.Precautions & WarningsFor ophthalmic use only. Patients should remove their contact lenses prior to instilling this preparation and should not insert their lenses until 15 minutes after instillation of the preparation.Storage ConditionsStore between 15-30?C. Protect from light.Use In Special PopulationsUse in children: Safety and effectiveness in children below the age of 2 years have not been established.?Use in elderly patients: No overall differences in safety and effectiveness have been observed between elderly and other adult patients.Drug ClassesDrugs for miotics and glaucomaMode Of ActionDorzolamide, a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, has actions similar to acetazolamide. By inhibiting carbonic anhydrase in the ciliary processes of the eye, dorzolamide decreases aqueous humor secretion. Used together, there is additional intraocular pressure reduction compared to using either component alone, but the reduction is not as much as concomitant admin of dorzolamide tid and timolol bid.Timolol maleate, a nonselective ?-adrenergic blocker, reduces aqueous humor formation.PregnancyUse in pregnancy: There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. This Eye Drops should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.?Use in lactation: Caution should be exercised when This Eye Drops is administered to a nursing mother.Pediatric UsesUse in children: Safety and effectiveness in children below the age of 2 years have not been established.?Use in elderly patients: No overall differences in safety and effectiveness have been observed between elderly and other adult patients.Sku: 1736098143-1708
Azopt2%+0.5%
₦33,000.00Original price was: ₦33,000.00.₦29,700.00Current price is: ₦29,700.00.₦33,000.00Original price was: ₦33,000.00.₦29,700.00Current price is: ₦29,700.00. Add to basket Quick View